Learning Local Shape Descriptors from Part Correspondences
With Multi-view Convolutional NetworksHaibin Huang1, Evangelos Kalogerakis1, Siddhartha Chaudhuri2, Duygu Ceylan3, Vladimir G. Kim3, M. Ersin Yumer 3
ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2017 (also presented in SIGGRAPH 2018).
University of Massachusetts Amherst1 , Indian Institute of Technology Bombay2, Adobe Research3
Abstract
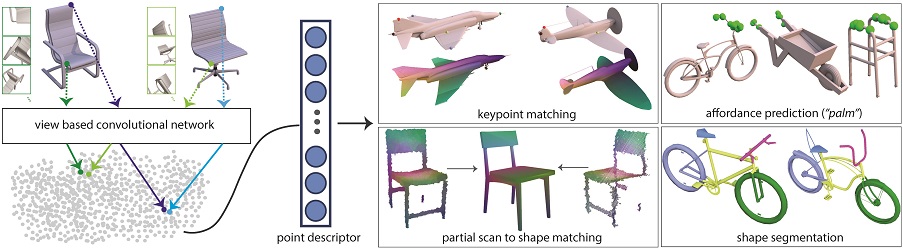
We present a new local descriptor for 3D shapes, directly applicable to a wide range of shape analysis problems such as point correspondences, semantic segmentation, affordance prediction, and shape-to-scan matching. Our key insight is that the neighborhood of a point on a shape is effectively captured at multiple scales by a succession of progressively zoomed out views, taken from care fully selected camera positions. We propose a convolutional neural network that uses local views around a point to embed it to a multidimensional descriptor space, such that geometrically and semantically similar points are close to one another. To train our network, we leverage two extremely large sources of data. First, since our network processes 2D images, we repurpose architectures pre-trained on massive image datasets. Second, we automatically generate a synthetic dense correspondence dataset by part-aware, non-rigid alignment of a massive collection of 3D models. As a result of these design choices, our view-based architecture effectively encodes multi-scale local context and fine-grained surface detail. We demonstrate through several experiments that our learned local descriptors are more general and robust compared to state of the art alternatives, and have a variety of applications without any additional fine-tuning.
